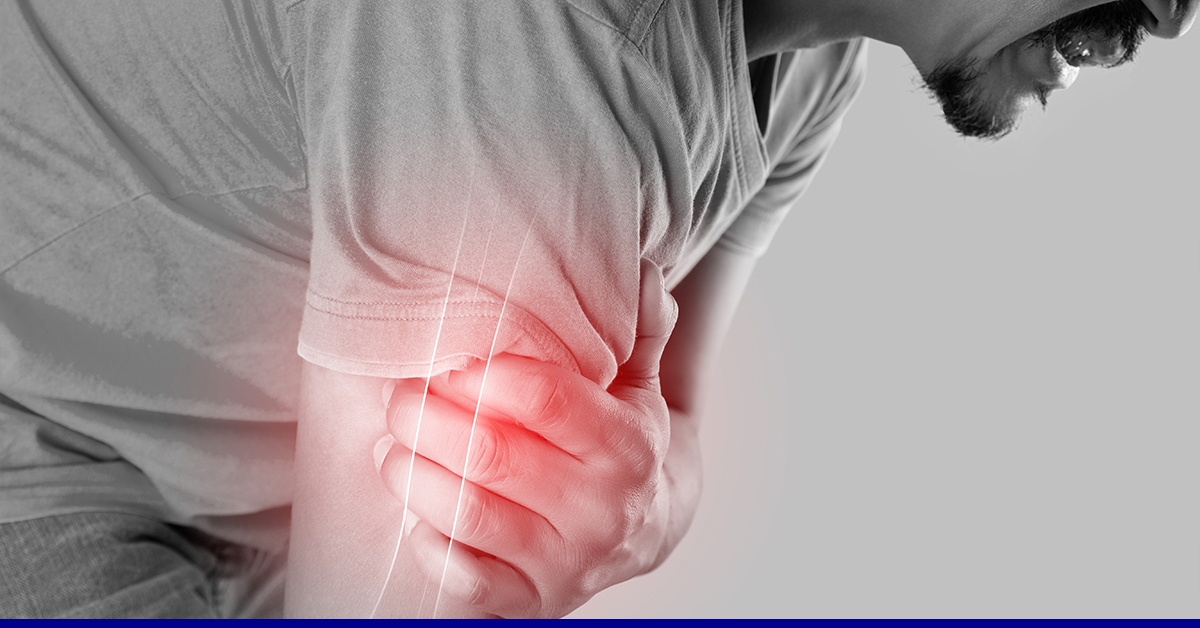
Myositis is a broad term for persistent, increasing muscular inflammation. Skin rashes are connected with several kinds of myositis. This uncommon condition can be hard to identify, and the reason is not always recognized. Symptoms might arise suddenly or gradually. Myositis symptoms may include muscle discomfort and soreness (myalgias myositis), weariness, difficulty swallowing, and trouble breathing, some of the primary symptoms.
In the United States, an estimated 1,600 to 3,200 new cases are diagnosed yearly, with 50,000 to 75,000 people living with myositis disease. Either children or adults can be affected by myositis. Except for one kind of myositis, women are more likely than males to be afflicted by this myositis disease.
Dermatomyositis is the most easily diagnosed kind of myositis disease due to the purple-red lesions in the shape of a heliotrope flower. The rash appears on the eyelids, the face, the chest, the neck, and the back. It also appears on the knuckles, elbows, knees, and toes. Muscle weakness is usually the result.

Polymyositis symptoms begin with muscular weakness closest to the body’s trunk and gradually spread. Each instance is distinct, and persons with polymyositis disease are frequently discovered to have other autoimmune disorders.
Juvenile myositis affects children under the age of 18. It affects between 3,000 and 5,000 American youngsters. Girls are twice as likely as boys to get JM. Like the other types of myositis, JM causes muscle weakness and skin rashes. Juvenile myositis symptoms share symptoms of overall types of myositis.
Some prescription medicines and illegal narcotics are suspected of inducing toxic myositis. Statins, which decrease cholesterol, may be among the most prevalent medicines to induce this syndrome. Other drugs and chemicals that may induce myositis, albeit exceedingly rare, include:
Toxic myositis symptoms are similar to that of other kinds of myositis. People who have this illness usually improve if they stop taking the medicine that caused the poisoning.
Inclusion-body myositis disease seems to be the only myositis that affects males more than women. The majority of those who get this illness are above the age of 50. This begins with wrist and finger weakness and thigh muscular weakness. Muscle weakness is more noticeable in small muscles and also is asymmetrical, affecting one side of the body more than the other. IBM is thought to be genetic.
Myositis disease is caused by a variety of factors, according to experts. Myositis is regarded to be an immunological disorder in which the body attacks the muscles. The majority of cases have no recognized cause. Injury and illness, however, are considered to play a role. According to some studies, myositis could also be produced by autoimmune illnesses such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus viruses like the common cold and flu, as well as HIV medication toxicity.
Patients with myositis disease are frequently misdiagnosed. Myositis can be hard to diagnose due to its rarity and the predominant symptoms of muscular weakness and tiredness. Myositis symptoms can be observed in a variety of different prevalent disorders.
Physicians can utilize any of the below options to help them make a diagnosis:
Myositis disease and its symptoms are not treated with any specific drugs. Corticosteroids, such as prednisone (Rayos), are commonly given. Doctors frequently use this medication with immunosuppressive medications like azathioprine (Azasan) and methotrexate (Trexall). Because of the nature of this condition, it may take multiple modifications in treatment for a doctor to determine the best plan of care for you. Work with your doctor to determine the best course of action. Physiotherapy, exercising, stretching, and meditation can assist in maintaining muscular strength and flexibility and could help relieve the myositis symptoms and the disease itself while preventing muscle atrophy.
In most circumstances, medications are used to alleviate pain and symptoms of illness. Most patients with myositis respond to therapy even in the most severe instances. You may need to try various treatments before you find one that works best for you. It may take longer to regain muscle strength. Exercises can assist in enhancing muscular strength if myalgias or myositis has been managed with medication.
Although some people recover fully, others never regain their normal muscular power or function.
See Also: Occupational Therapy Verses Physical Therapy: Know The Difference
Myositis has no known absolute treatment though symptoms could be relieved. Myositis patients may need to use a cane, stroller, or wheelchair. Myositis, if left untreated, can result in disability and even death. Some people, however, can effectively control their symptoms. Some people may even have partial or total remission.